
Last-Mile Delivery Market Size: Growth Trends, Projections & More

Wise Systems
Last-Mile Delivery Market Size: Growth Trends, Projections & More

Wise Systems

The last-mile delivery market has become a core component of the global logistics industry, handling the timely delivery of goods to end consumers. As the e-commerce sector thrives and consumer expectations rise, the final-mile delivery market is experiencing sustained growth and innovation. Continue reading to explore the key segments, delivery modes, service types, trends, and technologies shaping this market.
In this article:
- Market Size and Projections
- Global Perspectives on e-Commerce Growth
- Key Market Segments
- Delivery Modes
- Vehicle and Service Types
- Market Trends
- Ride the Wave
- Frequently Asked Questions
Market Size and Projections
The final-mile delivery sector has always existed in some form, but in the last few years, the volume of parcels transported within this final leg has reached unprecedented levels. In 2021, the market was valued at a remarkable $131B. This substantial market size reflects the increasing importance of efficient and reliable last mile logistics in the modern retail landscape.
Looking ahead, the global final mile delivery market is anticipated to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.13% from 2022 to 2031.
Global Perspectives on e-Commerce Growth
The last-mile delivery market is a global industry with multiple regional segments. Each region has its unique characteristics, influenced by factors such as infrastructure, consumer behavior, and local regulations. However, all regions are experiencing growth in step with the surge in e-commerce and the increasing demand for fast delivery services.
1. North America (NA)
The North American region, particularly the United States, has seen a significant increase in e-commerce sales and home deliveries. By the third quarter of 2022, U.S. e-commerce retail sales hit a staggering $250 billion, reflecting an impressive 10% increase compared to the same period the previous year. US e-commerce surpassed $1 trillion for the first time in 2022 and is continuing to expand YOY at a rate of 7.7%. The key drivers for this expansion are price and speed. Customers can scrounge around for the best deals online and get their goods delivered super fast – sometimes even on the same day.
2. Asia-Pacific (APAC)
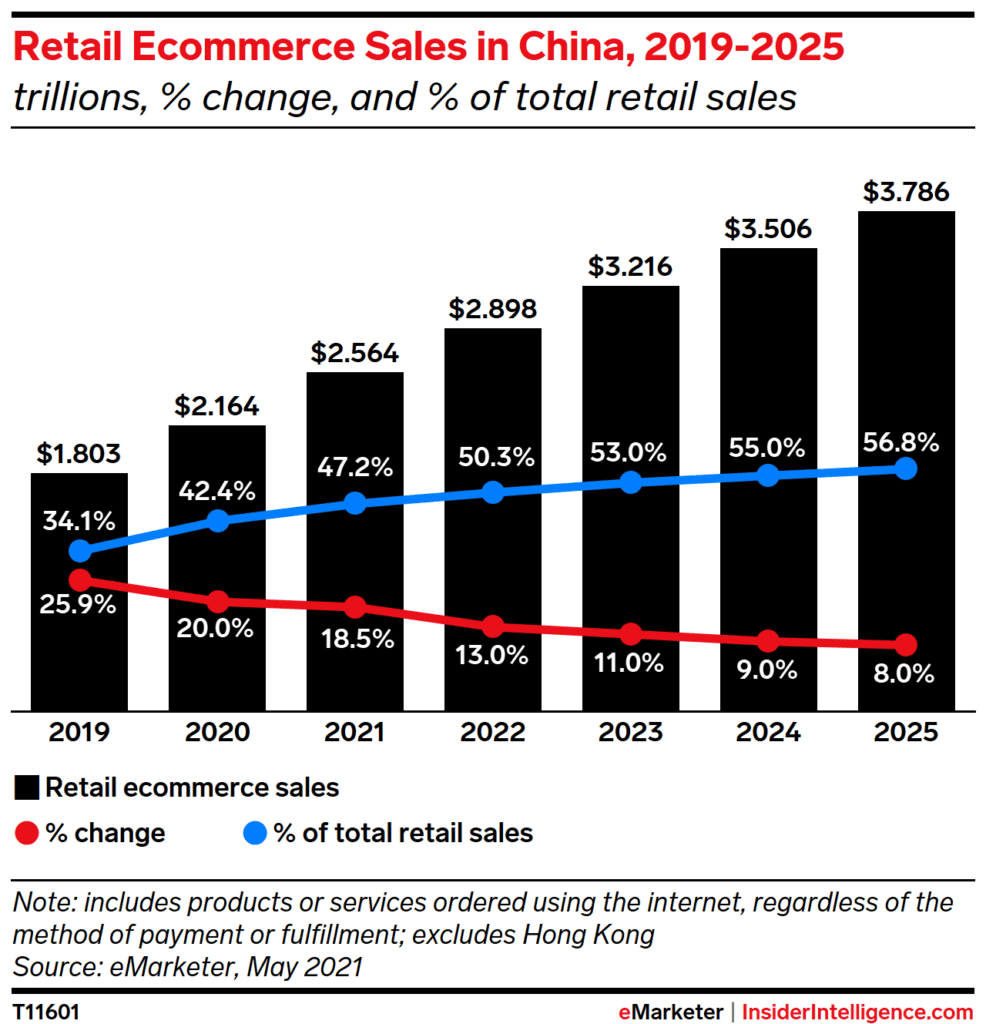
The Asia-Pacific last-mile delivery market is currently the market leader and growing faster than all other regions. This is attributed to robust interest in e-commerce within China. China alone generates almost 50% of all transactions worldwide.
The Chinese e-commerce market is dominated by Alibaba’s Taobao and Tmall, accounting for 50.8% of the market share. Revenue is expected to continue its upward trend, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.17%. Sales are expected to pass the $3 billion mark in 2024. Electronics, fashion, and toys/hobby items are the leading categories within the APAC market.
3. Europe (EMEA)
According to Mordor Intelligence, the last delivery market in the European region is currently valued at $599 billion and is projected to reach $880 billion by 2028. While this lags behind the United States and other developed geographical regions, the strict Covid-19 lockdown measures and widespread internet penetration has fostered e-commerce growth within the European market. Key countries like the United Kingdom, Germany, France, Spain, and Italy are the leading contributors to the e-commerce surge in the region.
4. Latin America (LAD)
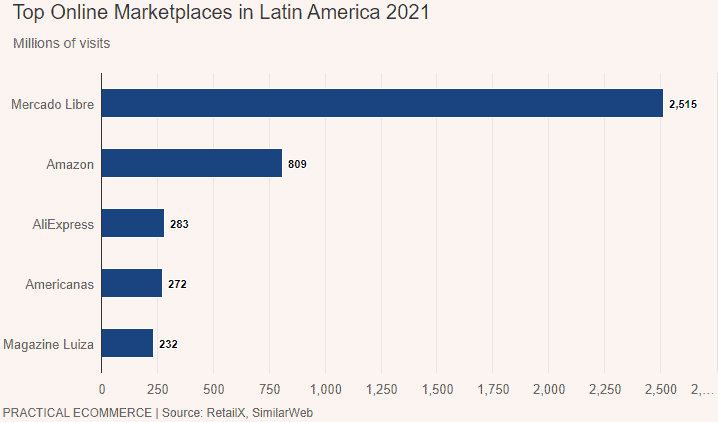
The Latin American market encompasses several companies, from Peru and Argentina to Chile, Colombia, and Brazil. While the e-commerce sector is growing in this region, it remains relatively small, with retail sales reaching approximately $121 billion by 2023. There are numerous obstacles hindering the kind of expansion seen in other regions.
Only 79% of the population has internet access, and roughly 50% have no bank account. Rural areas suffer from poor infrastructure, making it difficult to support delivery services on unpaved roads.
One online marketplace service in Latin America, Mercado Libre, has found a path to success by focusing on logistics and improving delivery times. Mercado Libre saw a 58% increase in revenues between 2020 and 2021, signaling a substantial demand for e-commerce services in the region.
5. Middle East and Africa
In the Middle East and Africa, e-commerce platforms face significant challenges when trying to expand their operations to this region. The main obstacle is the lack of adequate infrastructure to support last mile deliveries.
e-Commerce is predicted to grow substantially in the Middle East, reaching $100 billion by 2025. However, companies have to deal with high delivery costs. Shipping a single parcel can cost between $10 to $15, with a 2-3 delivery timeline. A notable 70% of customers desire same-day delivery and are willing to pay extra for it. Unfortunately, the current infrastructure is not well-equipped to meet this demand at scale.
The situation is similar in Africa, where the last-mile delivery market is relatively small, amounting to just $1.14 billion in 2021. It is projected to increase to $2.35 billion by 2030.
Key Market Segments
The market can be segmented into three key areas, known as Business-to-Consumer (B2C), Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C), and Business-to-Business (B2B).
B2C Delivery
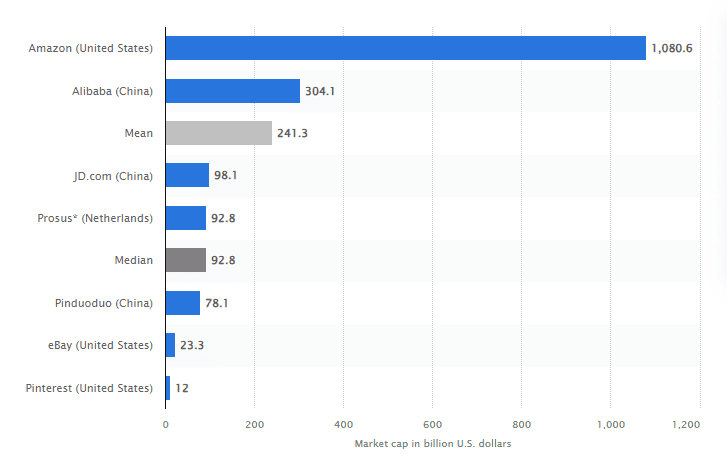
The B2C segment focuses on delivering products directly to individual customers. e-commerce giants like Amazon, Walmart, Alibaba, and Target have transformed the retail sphere with their vast product offerings and efficient delivery networks. As of June 2022, Amazon is the biggest player in the e-commerce market, with a market cap of around $1B, far surpassing the second biggest market cap from Alibaba at $300M.
With advanced logistic systems and partnerships with shipping providers, these companies provide seamless B2C doorstep delivery for their online stores.
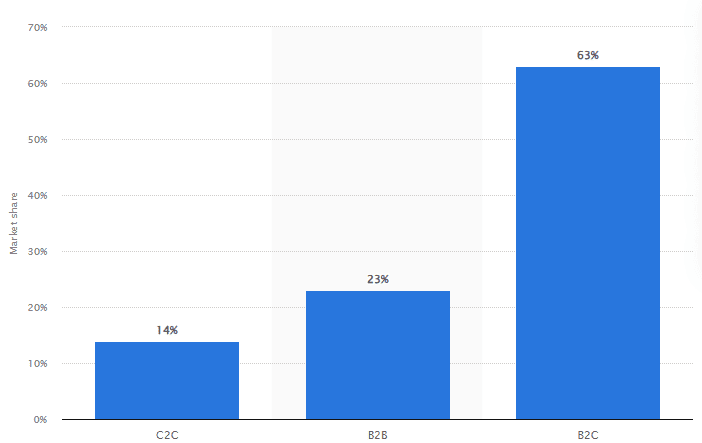
Regarding the characteristics of these deliveries, the volume is high, to the tune of millions of packages daily and accounting for 63% of all deliveries in 2018, while the value varies considerably. Platforms may facilitate the sale of high-value times like electronics, luxury goods, and high-end fashion.
B2B Delivery
In addition to the B2C and C2C segments, there is another segment known as Business-to-Business (B2B) delivery. This segment involves the transportation of bulk orders, supplies, raw materials, and other goods needed for business operations. B2B deliveries often require specialized handling, including palletization and supplier coordination. These deliveries are typically handled by logistics providers that specialize in B2B operations, offering services like freight forwarding, warehousing, and distribution.
While B2B delivery may not dominate the last mile market in terms of volume, it plays a crucial role in supporting businesses and supply chains.
C2C Delivery
This segment focuses on the transportation of goods between individual consumers. The rise of peer-to-peer (P2P) marketplaces like eBay, Poshmark, Mercari, Facebook Marketplace, Depop, and OfferUp have enabled seamless transactions and expanded opportunities for buyers to purchase items from individual sellers.
The categories that see the most sales in the C2C market are fashion, family-related items such as toys, and beauty and personal care products.
C2C deliveries may not reach the same magnitude as B2C, but it still makes up a substantial volume considering the multitude of transactions across many smaller sellers. Consumers are keen to save money and contribute less to wasteful economies.
The C2C market exploded during Covid-19, and for Europe alone, the market is already exceeding $6.6 billion in volume.
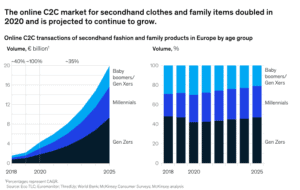
Most shipments are small-scale, with a few items at most. These deliveries are generally handled by delivery service providers USPS, UPS, FedEx, or DHL after being packaged and dropped off by sellers.
Delivery Modes
In the last mile market, businesses have several options for choosing the most suitable delivery mode based on their specific needs, budget, requirements, and customer expectations. These different delivery modes offer unique benefits and considerations.
- Conventional – Traditional courier services involve the use of delivery personnel or postal services for transporting packages. While Amazon has created its own fleet of delivery vans, most businesses still use USPS, FedEx, or one of the other established options. Fedex alone handles roughly 111,000 shipments per day, while Amazon handles approximately 66,000 orders per hour.
- Third-Party Logistics – Outsourcing is big business. By some estimates, 81% of businesses outsource their domestic shipping to 3PL providers, although more conservative estimates fall at around 33%. These companies specialize in managing the logistics and transportation aspects, including route optimization, delivery scheduling, and driver management.
By partnering with 3PL providers, businesses can benefit from their expertise, infrastructure, and established networks. The global market for 3PL is projected to reach $2.8 trillion by 2031, thanks to a CAGR of 8.8%.
- In-house Delivery – Some companies choose to establish their own in-house delivery fleet. This mode provides complete control over the delivery process, allowing businesses to tailor operations to their specific requirements.
In-house delivery involves hiring and managing delivery personnel, maintaining a fleet of vehicles, and implementing logistics management systems. According to APQC, 42% of businesses utilize an in-house delivery fleet.
- On-Demand – 90% of shoppers expect two or three-day shipping. To accommodate these short delivery timeframes, local delivery partners with on-demand delivery are increasingly common. With a vast network of delivery partners, on-demand platforms can dispatch the nearest available driver to pick up an order from a retail store or distribution center and deliver it to the customer.
These drivers typically use their personal vehicles and may carry a dozen or so packages. This immediacy is particularly useful when the customer has paid extra for quick delivery.
Vehicle and Service Types
To go along with the different delivery modes, there is a range of vehicle and service types to choose from. Historically box trucks have been the primary method, but this is changing and diversifying to meet market demands.
- Conventional – Due to their versatility and cargo capacity, traditional vehicles, such as vans and trucks, remain the primary mode of transportation for last-mile delivery services. These vehicles are ideal for handling larger and bulkier items, although their fuel efficiency leaves much to be desired.
- Personal Vehicles – Another mode of transportation for last-mile delivery involves personal vehicles. This mode taps into the gig economy, allowing individuals to use their cars for delivery services. This method offers flexibility and scalability, although it can introduce challenges related to insurance and driver availability during peak hours.
- Micro-Mobility – This service type has become a promising option in dense urban areas. Delivery companies are employing electric bikes, scooters, and even electric skateboards to navigate congested city streets. These compact and agile vehicles reduce traffic congestion, lower emissions, and are suitable for delivering small to medium-sized and time-sensitive packages.
- Eco-Friendly – There is pressure on the industry to shift toward more eco-friendly transportation options. Electrical vehicles (EVs) offer numerous advantages, including zero-emission operation and reduced costs.
Most players in the final mile delivery market have recognized the potation of EVs and have started incorporating them into their fleets. For instance, Amazon has pledged to have 100,000 electric Rivian vans on the road by 2030.
Market Trends
Last-mile delivery is a quickly evolving market, moving to keep pace with changing customer expectations and increasing e-commerce sales. It’s hard to know what trends will arise in the future, but a few emerging trends have already taken root.
- Same-Day and Instant Delivery – These days, customers expect their package to arrive on their doorstep within 48 hours, thanks to Amazon’s overnight, same-day, and next-day delivery options. Companies are investing in technology and operational strategies to offer these options, including hyperlocal fulfillment centers and automated sorting facilities.
- Smart Lockers and Pickup Points – Alternative delivery locations are becoming more prevalent as a convenient and secure last-mile delivery option. Over 70,000 of these lockers are placed around the US, often in central areas or retail stores, allowing customers to pick up their packages at a time that suits them best. This reduces the need for home deliveries and minimizes the risk of stolen packages.
- Contactless Delivery – Since the Covid-19 pandemic, contactless delivery has become a standard delivery practice. Many delivery companies now provide photographic proof of delivery after dropping packages on a doorstep. This trend not only caters to the health and safety concerns of consumers but also enhances the overall customer experience by offering a non-disruptive and speedy delivery.
Ride the Wave
As the last-mile delivery market continues to grow year over year, businesses have a unique opportunity to ride the wave of this expansion and position themselves for success. The Wise Systems delivery automation platform and its AI-powered Dynamic Optimization Engine (DOE) is at the forefront of enabling businesses to capitalize on this market surge.
By leveraging the cutting-edge technology and capabilities of the Wise Systems platform, businesses can overhaul their delivery operations and exceed their customer’s expectations. Wise Systems offers real-time visibility, route optimization tools, predictive analytics, and more.
Request a demo today to embark on a journey toward optimized deliveries and increased customer satisfaction. Wise Systems is here to help to make the most of the market boom and propel your business to new heights.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the market size of last-mile delivery in 2030?
Various research groups have estimated the expected last-mile delivery market size. Projections differ depending on the source.
According to a news release from Precedence Research (published by Globe Newswire), the global last-mile delivery market size is expected to reach $297 billion by 2030. The last-mile delivery market size is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.6% from 2022 to 2030.
Another research group, Transparency Market Research, projects that the global last-mile delivery market will expand from $191.4 billion in 2022 to $291.9 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 4.8% throughout the forecast period.
How much is the last-mile market worth?
Precedence Research estimates that the last-mile market is worth approximately $142.9 billion as of 2022. Transparency Market Research estimates the last-mile market at a higher value, approximately $191.4 billion as of 2022.
What is the market size of big and bulky last-mile delivery?
The big and bulky last-mile delivery market has been one of the fastest-growing 3PL segments since 2017 and is expected to continue strong growth through 2025.
According to Armstrong & Associates, the 3PL big and bulky last-mile delivery market in the U.S. is worth an estimated $9.3 billion as of 2022. The U.S. 3PL big and bulky last-mile delivery market grew at a CAGR of 18.2% from 2017 to 2022 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 11.8% from 2022 to 2025.
What is the market size of the delivery industry?
According to IBISWorld, the global courier and delivery services industry is valued at an estimated $482.9 billion as of 2023. The global courier and delivery services industry has grown at an average of 5.0% per year from 2018 to 2023 (faster than the economy overall), and in 2023, it’s projected to increase 2.5%.

